Working with React.js Class Components
React.js is a first class JavaScript library for building front-end for the modern web applications. This library is based on a WebComponent concept. The WebComponent is an autonomous object which has it own UI, Data and logic (presenter). The React.js is makes use of this concept to implement <b>Compositional UI<b>.
In React.js, we can create components using 2 mechanisms, the first is Class Component and the second is Functional Components.
Class Components, are the pure implementation of ES 6 class concept. The class component is derived from Component base class. This base class contains render() method to render the HTML UI. The class components defines local public properties. These properties represents State of the class component. The State, means the data that will be used by class component to manipulate local to component so that the the HTML UI can be rendered.
Functional Components, are the JavaScript functions. These functions returns the HTML so that the UI will be rendered. While working with React.js applications, you can use either of the components. The functional components uses a concept of React.js Hooks to define state, making AJAX calls, etc.
One important of the React.js library is that, it uses the concept of Virtual DOM. This means that, the DOM rendering is manipulated based on the State data bound with HTML elements. The DOM will be rendered in the browser based on the virtual DOM. If the data bound property of the HTML element is changed, then new Virtual DOM rendering will be compare with the previous Virtual DOM rendering and instead of re-rendering the whole DOM, only the updated data bound HTML will be patched into the rendering. This will provide a reactive UI generation for the front-end applications.
Being compositional in nature, we can create re-usable components in React.js applications. This will help to divide the complex UI in small chunks of components and we can share these components across various projects in organisation or even we can share it to our customers. When we create and share re-usable components, we may need to pass data across components. We do this by using props or using context. So the question is what is the difference between State and Props.
State: This is an object that is scoped to the component. This object contains all properties those will be having their lifecycle within the component itself. Once the component is unloaded (aka unmounted), the state will be cleaned.
Props: This will be used to maintain the state of the data across components. The container / parent component can send data to child component using props. The props are shared in a hierarchy of all components in the React.js applications.
In this post, I will demonstrate class components. The post contains code with component re-usability. we will create the React.js application using the React.js CLI.
Step 1: Open Command prompt (Windows Command Prompt / Terminal Window in Mac or Linux) and run the following command to install React CLI
npm install -g create-react-app
Once the React CLI is installed, we can use it for creating React.js applications.
Step 2: On the command prompt, run the following command to create a new React project.
create-react-app my-react-app
The new application will be created with the folder name as the name of the application. Open the my-react-app folder in Visual Studio Code (VSCode).
Navigate to the project folder in the command prompt and run the following command to install Bootstrap CSS framework so that we can use it in our application
npm install --save bootstrap
Step 3: In the project, we have the src folder. In this folder add a new folder and a new folder and name it as components. In this folder add a new file and name this file as dropdowncomponent.jsx. In this file we will add a class component. This class component will be used as reusable DropDown. In this file add a code as shown in the listing 1
Listing 1: The DropDownComponent
The DropDownComponent class is derived from Component base class. The constructor accepts the props parameter. This parameter will be used when the parent of this component pass any data to the DropDownComponent. Note that there is no state property declared for this component. The render() method returns <select> element. This select element will generate <options> based on the data passes to this component from its parent component using the dataSource property. Here in this case the dataSource property is a props type property. The handleChange() method is bound to the onChange event of the <select> element, so that when a value is chosen from the <select> element it will be emitted back to the parent component. The code
this.props.selectedValue(evt.target.value);
define the selectedValue props type. The parent component can read the selected value from the DropDownComponent by using the selectedValue props type.
Step 4: In the components folder add a new file and name this file as tablecomponent.jsx. In this component we will generate the HTML table element dynamically. Like DropDownComponent, the TableGridComponent is also a re-usable component. This will accept props type from its parent to generate the HTML table dynamically. In the tablecomponent.jsx file add the code as shown in listing 2
Listing 2: The TableGridComponent
The TableGridComponent reads the data from the dataSource props type and generate table headers and rows. The table row is bound with the handleRowClick() method using the onClick event. When the row is clicked the selected record which is bound with the Table row will be passed to the selectRow() props type so that the parent component can receive the selected value from the TableGridComponent.
Step 5: In the src folder add a new folder and name it as models. In this folder add a new file and name it as product.js. In this file add a code for Product class as shown in listing 3
Listing 3: The Product Class
Add one more file in the same folder and name it as constants.js. In this file we will define constant array as shown in listing 4
Listing 4: The constants
Add one more file in the models folder and name it as logic.js. This file will contains a code for logic for Read/Write operations for Product. The code of the logic is provided in listing 5
Listing 5: The Logic class
Step 6: In the components folder add a new file and name it as productformcomponent.jsx. In this flde we will create a ProductFormComponent. This component will use DropDownComponent and TableGridComponent and also the logic class. Add the code in this file as shown in listing 6
Listing 6: The ProductComponent class
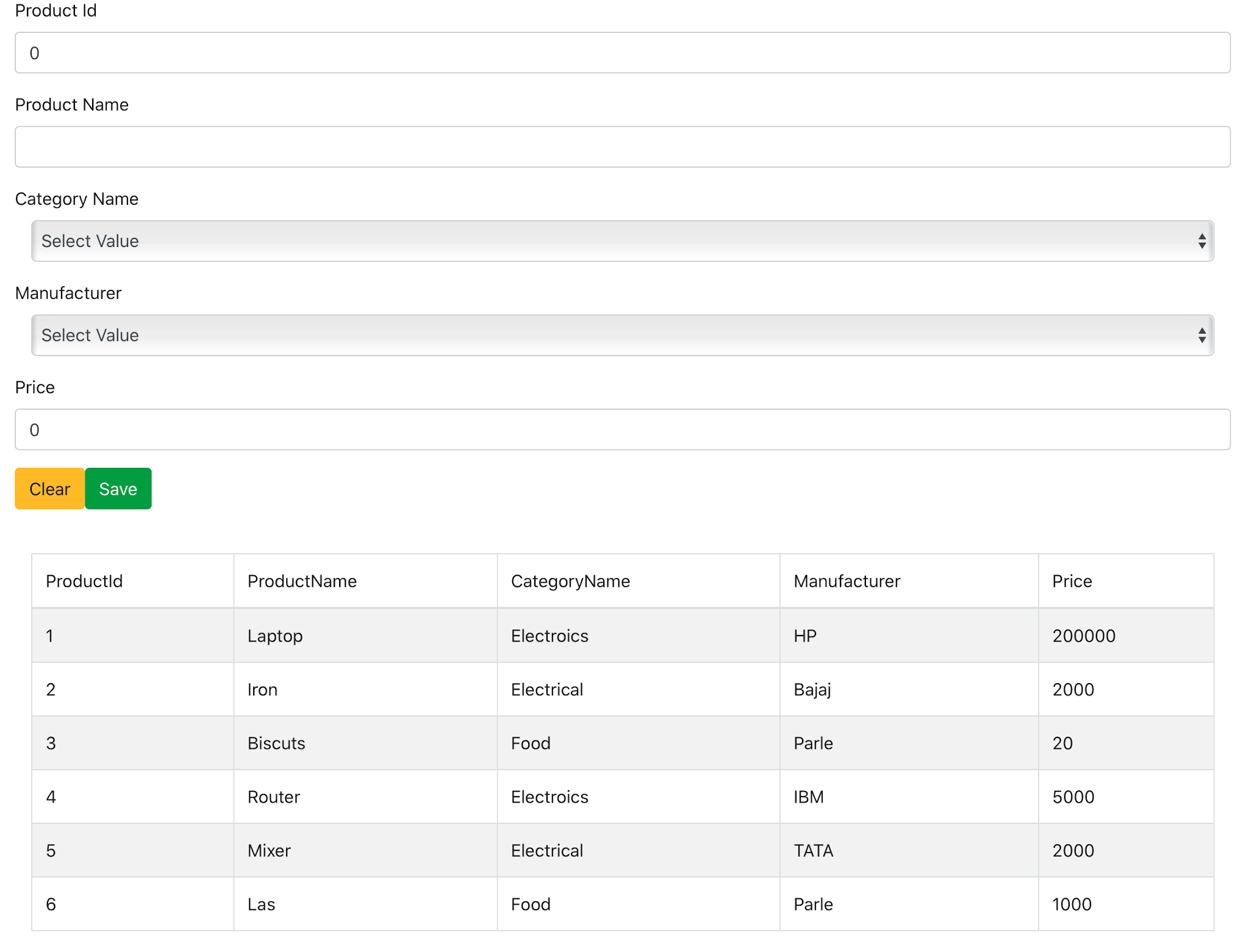
The ProductFormComponent defines the state properties for Product information, categories, manufacturers and products. The component contains methods clear(), save() to clear all HTML input elements and save product data. The getCategory() and getManufactuer() methods are bound to DropDwonCompoent used in render() method. This component is used twice in the ProductFormComponent to show categories and manufacturers arrays passed to this component using the dataSource props type. The selected category and manufacturer will be received by the ProductFormComponent using the getCategory() and getManufactuer() methods. The TableGridComponent accepts products data using the dataSource props type to render the HTML table to show products data. The Save and Clear buttons are bound to save() and clear() methods using its onClick event.
So, if you have notices that, we have design a React component that re-uses the other React components in it and hence we can say that React.js is compositional in nature.
Step 7: Modify index.js to run the ProductFormComponent and also load the bootstrap.css as shown in listing 7
Listing 7: Index.js
Run the application using following command
npm run start
The browser will be opened with an address in address bar as http://localhost:3000
The browse will render the ProductFormComponent as show in image 1
Image 1: The ProductFormComponent
Conclusion: React.js compositional nature allows us to create re-usable components. The class components provides a simple Object-Oriented-Programming like experience to create a React front-end application with an experience like server side programming.